Skin Cancer on Lip: A Comprehensive Guide to Detection, Treatment, and Prevention
Skin cancer on the lip, a form of squamous cell carcinoma, is a prevalent type of cancer that affects the skin of the lips. It often manifests as a persistent scab or sore that fails to heal. The condition is particularly concerning due to its potential to spread to other parts of the body if left untreated.
Understanding skin cancer on the lip is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. This article will delve into its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures to empower individuals with the knowledge necessary to safeguard their lip health.
Skin Cancer on Lip
Skin cancer on the lip encompasses various essential aspects that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of this condition. These elements play a vital role in detection, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Risk Factors
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Prevention
- Prognosis
- Complications
- Epidemiology
- Research
Each of these aspects holds significance in the context of skin cancer on the lip. Symptoms aid in early detection, while causes and risk factors provide insights into preventive measures. Diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment selection, leading to better outcomes. Prevention strategies, including sun protection and lifestyle modifications, are crucial in reducing the risk of developing the condition. Understanding prognosis and potential complications helps individuals make informed decisions about their treatment and care. Research advancements contribute to the development of novel therapies and a deeper understanding of the disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms play a pivotal role in early detection of skin cancer on the lip. Recognizing and understanding these signs can prompt timely medical attention, leading to a better prognosis.
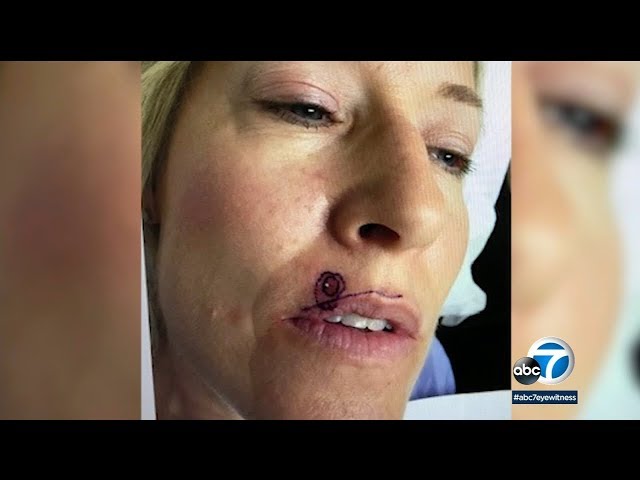
- Persistent Sore: A non-healing sore or ulcer on the lip that persists for more than two weeks may be a symptom of skin cancer. It may appear as a red, scaly patch or a white or yellowish lesion.
- Lip Lump or Bump: A painless lump or bump on the lip that gradually enlarges can also be a sign of skin cancer. It may be firm to the touch and may bleed or crust over.
- Lip Bleeding or Crusting: Unexplained bleeding or crusting on the lip that does not resolve with time may be a symptom of skin cancer. It may occur spontaneously or after minor trauma.
- Lip Numbness: Numbness or loss of sensation in the lip can be a sign of advanced skin cancer. It occurs when the cancer affects the nerves in the lip.
These symptoms, while not exclusive to skin cancer, warrant medical evaluation to rule out any underlying malignancy. Early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes in skin cancer on the lip.
Causes
Understanding the causes of skin cancer on the lip is key to developing effective prevention strategies and improving treatment outcomes. Various factors, both intrinsic and extrinsic, can contribute to the development of this condition.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Prolonged exposure to UV rays from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds, is a major cause of skin cancer on the lip. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause uncontrolled cell growth.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer on the lip. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the DNA in lip cells and suppress the immune system, making the body less able to fight off cancer cells.
- HPV Infection: Infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly types 16 and 18, has been linked to an increased risk of skin cancer on the lip, especially among younger individuals. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can also be spread through contact with infected skin.
- Lip Trauma: Chronic irritation or injury to the lip, such as from ill-fitting dentures or braces, can contribute to the development of skin cancer. Repeated trauma can damage the lip tissue and create a favorable environment for cancer cells to grow.
These causes, acting alone or in combination, can significantly increase the risk of developing skin cancer on the lip. Understanding these factors and adopting preventive measures, such as sun protection, smoking cessation, HPV vaccination, and avoiding lip trauma, are crucial for reducing the incidence of this potentially serious condition.
Risk Factors
Risk factors play a crucial role in the development of skin cancer on the lip. They increase the likelihood of an individual developing the condition, although their presence does not guarantee its occurrence. Understanding these risk factors is essential for preventive measures and targeted interventions.
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a primary risk factor for skin cancer on the lip. Prolonged sun exposure damages the DNA in lip cells, leading to mutations that can cause uncontrolled cell growth. Individuals with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or frequent outdoor activities are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer on the lip.
Tobacco use, including smoking and smokeless tobacco, is another significant risk factor. The chemicals in tobacco smoke and smokeless tobacco can damage the DNA in lip cells and suppress the immune system, making the body less able to fight off cancer cells. Smokers are at a significantly increased risk of developing skin cancer on the lip compared to non-smokers.
In summary, understanding risk factors for skin cancer on the lip is essential for prevention and early detection. Avoiding excessive sun exposure, quitting tobacco use, and regular lip examinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing this potentially serious condition.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis plays a critical role in the management of skin cancer on the lip, as it determines the appropriate treatment plan and prognosis. An accurate and timely diagnosis can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes and prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. The diagnosis of skin cancer on the lip typically involves a combination of physical examination, biopsy, and imaging tests.
During a physical examination, a healthcare professional will visually inspect the lip and surrounding areas for any suspicious lesions or abnormalities. They may also palpate the lip to assess for any lumps or thickening. If a suspicious lesion is identified, a biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the lesion and examining it under a microscope to determine the presence of cancer cells.
Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, may be used to evaluate the extent of the cancer and determine if it has spread to other parts of the body. These tests can also help guide treatment planning and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
In conclusion, diagnosis is a critical component of skin cancer on the lip, as it provides essential information for making informed treatment decisions and predicting prognosis. Accurate and timely diagnosis can lead to improved patient outcomes and a better quality of life.
Treatment Options
Treatment options play a critical role in the management of skin cancer on the lip, aiming to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving the function and aesthetics of the lip. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and personal preferences.
Surgery is the primary treatment option for skin cancer on the lip. Surgical techniques range from simple excision of the cancerous lesion to more complex procedures involving reconstruction of the lip. Mohs micrographic surgery is a specialized surgical technique that allows for precise removal of cancerous tissue while preserving healthy tissue, resulting in better cosmetic outcomes.
Radiation therapy is another treatment option, particularly for larger or advanced tumors that are not suitable for surgery. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be delivered externally or internally, using radioactive implants placed near the tumor.
Other treatment options include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body, while targeted therapy and immunotherapy harness the body's immune system to fight the cancer. These treatments may be used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to improve outcomes.
Understanding the available treatment options for skin cancer on the lip is essential for informed decision-making. By carefully considering the factors involved and discussing the options with a healthcare professional, patients can choose the treatment that best meets their individual needs and goals.
Prevention
Prevention plays a crucial role in the fight against skin cancer on the lip, as it involves measures taken to reduce the risk of developing the disease in the first place. Understanding the strong connection between prevention and skin cancer on the lip is vital for individuals to make informed choices that can safeguard their lip health.
One of the most significant aspects of prevention lies in avoiding the primary risk factors for skin cancer on the lip, namely excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and tobacco use. Prolonged sun exposure damages the DNA in lip cells, while the chemicals in tobacco smoke suppress the immune system and promote cancer cell growth. By adopting sun-protective behaviors such as wearing sunscreen, seeking shade during peak UV hours, and avoiding tanning beds, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin cancer on the lip.
Real-life examples of prevention in action include public health campaigns that raise awareness about the dangers of UV radiation and tobacco use, encouraging individuals to adopt protective measures. Furthermore, the development of lip products with built-in sun protection factor (SPF) has made it easier for people to safeguard their lips while enjoying outdoor activities. These practical applications of preventive understanding have contributed to a decrease in the incidence of skin cancer on the lip.
In conclusion, prevention is a critical component of managing skin cancer on the lip. By understanding the connection between prevention and the disease, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk. Avoiding UV radiation, quitting tobacco use, and adopting sun-protective behaviors are essential strategies for preventing skin cancer on the lip, ultimately leading to better lip health outcomes.
Prognosis
Prognosis refers to the predicted course and outcome of a disease. In the context of skin cancer on the lip, prognosis plays a critical role in determining the appropriate treatment plan and predicting the likelihood of successful outcomes. A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between prognosis and skin cancer on the lip is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike.
The prognosis of skin cancer on the lip is influenced by various factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and response to treatment. Early detection and treatment significantly improve the prognosis, highlighting the importance of regular lip examinations and prompt medical attention for any suspicious lesions.
Real-life examples underscore the impact of prognosis on treatment decisions. For instance, a patient with a small, localized tumor confined to the lip may have a more favorable prognosis compared to a patient with a large, advanced tumor that has spread to other parts of the body. In such cases, the prognosis guides the choice of treatment, whether surgical excision, radiation therapy, or a combination of modalities, with the aim of achieving the best possible outcome.
Understanding the prognosis of skin cancer on the lip empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions about their care. It helps them navigate the treatment process with realistic expectations and prepare for potential challenges. Moreover, it informs resource allocation and research priorities, driving efforts towards developing more effective treatments and improving patient outcomes.
Complications
Skin cancer on the lip, though manageable when detected early, can lead to complications. Understanding the potential complications of skin cancer on the lip is crucial for informed decision-making and comprehensive patient care.
- Local Invasion: Skin cancer on the lip can invade surrounding tissues, including muscles, nerves, and even bone. This can lead to pain, disfigurement, and functional impairment, affecting speech, eating, and overall quality of life.
- Metastasis: In advanced stages, skin cancer on the lip can spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. Metastatic skin cancer is more difficult to treat and can be life-threatening.
- Recurrence: Even after successful treatment, skin cancer on the lip can recur. Regular follow-up examinations are crucial to detect and address recurrences promptly, improving the chances of successful outcomes.
- Treatment Side Effects: Treatment modalities for skin cancer on the lip, such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, can have side effects. These may include scarring, changes in lip sensation, dry mouth, and potential damage to healthy tissues.
The potential complications of skin cancer on the lip underscore the importance of early detection, timely treatment, and regular follow-up care. By understanding the risks and complications associated with this condition, individuals can make informed decisions, prioritize preventive measures, and actively participate in their treatment and recovery journey.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology plays a critical role in understanding the patterns, causes, and impact of skin cancer on the lip. It provides valuable insights into the factors that contribute to the development of this disease and helps guide preventive measures and treatment strategies.
One of the most significant contributions of epidemiology to skin cancer on the lip is the identification of risk factors. Through extensive research, epidemiologists have established a strong association between UV radiation exposure and the development of lip cancer. This understanding has led to public health campaigns emphasizing sun protection measures, such as wearing hats and sunscreen.
Epidemiology also helps monitor the incidence and prevalence of skin cancer on the lip over time. This information is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of prevention and treatment efforts. For instance, studies have shown a decline in lip cancer rates in recent years, likely due to increased awareness and adoption of sun-protective behaviors.
Moreover, epidemiology provides a platform for evaluating the effectiveness of different treatment options for skin cancer on the lip. By comparing outcomes among different patient groups, researchers can determine the most appropriate treatment approaches based on factors such as tumor stage, location, and patient characteristics.
In summary, epidemiology is an essential component of skin cancer on the lip. It helps identify risk factors, monitor disease patterns, and evaluate treatment effectiveness. This understanding informs preventive measures, guides clinical decision-making, and contributes to improved patient outcomes.Research
Research plays a pivotal role in the advancement of knowledge and understanding of skin cancer on the lip. It has significantly contributed to our current understanding of the causes, risk factors, and effective treatment approaches for this condition.
One of the most critical aspects of research in skin cancer on the lip is its focus on identifying risk factors and understanding the mechanisms underlying the development of the disease. Through extensive studies, researchers have established a strong association between UV radiation exposure and the development of lip cancer. This understanding has led to public health campaigns emphasizing sun protection measures, such as wearing hats and sunscreen.
Moreover, research has been instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of different treatment options for skin cancer on the lip. By comparing outcomes among different patient groups, researchers can determine the most appropriate treatment approaches based on factors such as tumor stage, location, and patient characteristics. This evidence-based approach has significantly improved treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
In summary, research is a critical component of skin cancer on the lip, driving advancements in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. It provides a systematic and rigorous approach to understanding the disease and developing effective strategies to combat it, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses frequently asked questions about skin cancer on the lip, providing concise and informative answers to clarify common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the early signs of skin cancer on the lip?
Answer: Early signs may include a persistent sore or lump on the lip, lip bleeding or crusting, and lip numbness.
Question 2: What are the risk factors for skin cancer on the lip?
Answer: Primary risk factors include excessive sun exposure, tobacco use, and certain types of HPV infection.
Question 3: How is skin cancer on the lip diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, biopsy, and imaging tests to assess the extent of the cancer.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for skin cancer on the lip?
Answer: Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
Question 5: Can skin cancer on the lip be prevented?
Answer: Preventive measures include avoiding excessive sun exposure, quitting tobacco use, and using lip products with SPF protection.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for skin cancer on the lip?
Answer: Prognosis depends on factors such as the stage and location of the cancer, but early detection and treatment generally lead to favorable outcomes.
These FAQs provide essential insights into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of skin cancer on the lip, empowering individuals with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their lip health. Understanding these aspects is crucial for early detection, timely intervention, and improved patient outcomes. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the latest advancements in research and explore specific case studies to further enhance our understanding of this condition.
Tips for Preventing Skin Cancer on Lip
Prevention is key in safeguarding your lip health. Here are some actionable tips to reduce your risk of developing skin cancer on the lip:
Limit sun exposure: Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially during peak hours. Seek shade, wear protective clothing, and use hats with wide brims.
Use sunscreens: Apply a lip balm or lipstick with SPF 30 or higher before going outdoors. Reapply frequently, especially after eating, drinking, or swimming.
Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and smokeless tobacco increase your risk of lip cancer. Quitting tobacco use is the most effective way to reduce your risk.
Get vaccinated against HPV: HPV infection is linked to lip cancer. Vaccination can protect against HPV strains that cause cancer.
Maintain good oral hygiene: Keep your lips clean and moisturized. Avoid biting or picking at your lips as it can damage the delicate skin.
Protect from wind and cold: Cold and windy conditions can dry out your lips, making them more susceptible to damage. Use lip balms with emollients to protect your lips.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer on the lip and maintain healthy, protected lips.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for successful skin cancer management. Regular lip examinations and seeking medical attention for any suspicious lesions are essential for your overall lip health and well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, skin cancer on the lip, while manageable, poses unique challenges that require a comprehensive understanding of its causes, risk factors, and treatment options. Prevention remains paramount, emphasizing sun protection, tobacco cessation, and HPV vaccination. Early detection and prompt intervention are crucial for favorable outcomes, highlighting the importance of regular lip self-examinations and seeking professional medical attention for suspicious lesions.
As research continues to unravel the complexities of skin cancer on the lip, advancements in treatment modalities and a deeper understanding of its biology hold promise for improved patient outcomes. By raising awareness, promoting preventive measures, and supporting research initiatives, we can collectively work towards a future where the impact of skin cancer on the lip is significantly reduced, safeguarding lip health and overall well-being.