The term "history of breast cancer ICD-10" refers to the historical evolution and classification of breast cancer using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). ICD-10 is a widely accepted medical coding system that assigns unique codes to diseases and health conditions for statistical and administrative purposes.
Understanding the history of breast cancer ICD-10 is crucial as it provides insights into the changing diagnostic criteria, disease classification, and treatment approaches over time. Studying historical developments can inform current practices, facilitate communication among healthcare providers, and support advancements in cancer research.
This article delves into the history of breast cancer ICD-10, exploring its significance, key developments, and implications for clinical management and research in breast cancer.
History of Breast Cancer ICD-10
Understanding the history of breast cancer ICD-10 offers valuable insights into the evolution of breast cancer diagnosis, classification, and management. Here are ten key aspects that highlight the significance of this topic:
- Diagnostic Criteria
- Disease Classification
- Treatment Approaches
- Coding Practices
- Statistical Analysis
- Research Trends
- Historical Context
- International Comparisons
- Clinical Implications
- Public Health Significance
These aspects encompass various dimensions of the history of breast cancer ICD-10, including the changing diagnostic criteria over time, the evolution of disease classification systems, the development of new treatment approaches, and the impact on coding practices and statistical analysis. Studying these aspects provides a deeper understanding of the historical context of breast cancer management, facilitates comparisons across different healthcare systems, and informs ongoing research and clinical decision-making.
Diagnostic Criteria
The evolution of diagnostic criteria for breast cancer, as reflected in the ICD-10 coding system, is a central aspect of the history of breast cancer ICD-10. Diagnostic criteria establish the parameters for identifying and classifying breast cancer cases, influencing treatment decisions, prognosis, and research.
-
Clinical Examination
The physical examination of the breast remains a cornerstone of breast cancer diagnosis. Palpation, inspection, and assessment of nipple discharge provide valuable information, guiding further diagnostic procedures.
-
Imaging Techniques
The development of imaging techniques, such as mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has revolutionized breast cancer diagnosis. These tools allow for the detection of tumors at earlier stages, leading to improved outcomes.
-
Biopsy
Biopsy, the removal of a tissue sample for microscopic examination, plays a crucial role in confirming breast cancer diagnosis. Types of biopsies include fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy.
-
Histopathology
Histopathology, the microscopic examination of breast tissue, is essential for determining the type and grade of breast cancer. It provides information about the cellular characteristics of the tumor, which guides treatment planning.
The evolution of diagnostic criteria for breast cancer ICD-10 has significantly improved the accuracy and early detection of the disease. This has led to better outcomes for patients, including increased survival rates and reduced morbidity.
Disease Classification
Disease classification plays a central role in the history of breast cancer ICD-10, providing a systematic framework for classifying and organizing breast cancer cases based on specific criteria. This classification system serves various purposes, including guiding treatment decisions, facilitating communication among healthcare providers, and supporting research and surveillance efforts.
-
Tumor Type
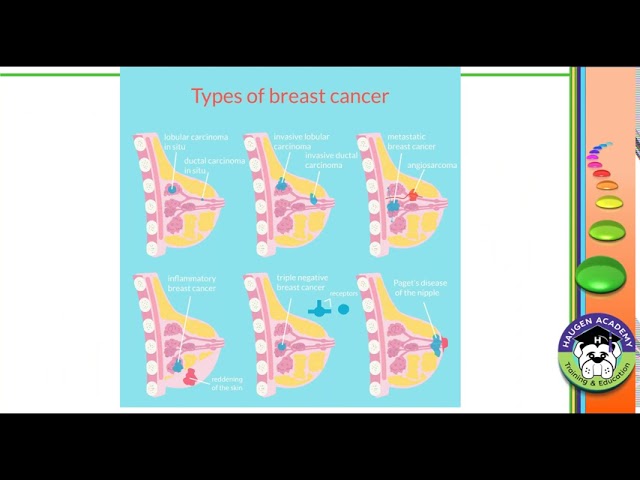
Breast cancer is classified into various types based on the characteristics of the tumor cells. The most common type is ductal carcinoma, which originates in the milk ducts. Other types include lobular carcinoma, inflammatory breast cancer, and Paget's disease of the breast.
-
Tumor Stage
Tumor stage describes the extent of cancer spread within the breast and surrounding tissues. The staging system considers factors such as tumor size, lymph node involvement, and distant metastases. This information guides treatment decisions and helps predict prognosis.
-
Histologic Grade
Histologic grade refers to the level of differentiation of tumor cells, which indicates the degree of abnormality compared to normal breast tissue. Grading systems assess factors such as cell size, shape, and arrangement. Higher grades generally indicate more aggressive tumors.
-
Molecular Subtype
Molecular subtyping classifies breast cancer based on the presence of specific genetic alterations and protein expression profiles. This information helps identify tumors with distinct biological characteristics, which can influence treatment selection and prognosis.
The evolution of disease classification in breast cancer ICD-10 reflects advances in our understanding of the disease. This refined classification system enables more accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment planning, and improved outcomes for patients with breast cancer.
Treatment Approaches
The evolution of treatment approaches for breast cancer, as documented in the history of breast cancer ICD-10, underscores the remarkable progress made in combating this disease. Various treatment modalities have emerged over time, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients.
-
Surgery
Surgery remains a cornerstone of breast cancer treatment, with the type of surgery depending on the stage and extent of the disease. Options include lumpectomy, mastectomy, and axillary lymph node dissection.
-
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be administered before or after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence or to alleviate symptoms.
-
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of cytotoxic drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is commonly used in combination with other treatments and can be administered orally or intravenously.
-
Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy is used to treat breast cancers that are fueled by hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone. It works by blocking the production or action of these hormones, slowing or stopping tumor growth.
The history of treatment approaches for breast cancer ICD-10 showcases the continuous advancements in medical science. As our understanding of breast cancer biology deepens, new and innovative treatment options continue to emerge, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for patients.
Coding Practices
Coding practices play a critical role in the history of breast cancer ICD-10. The accurate and consistent coding of breast cancer cases is essential for a variety of purposes, including:
-
Statistical analysis and disease surveillance
Coding practices provide the foundation for statistical analysis of breast cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality rates. This information is crucial for understanding the burden of breast cancer and evaluating trends over time.
-
Clinical research
Accurate coding is essential for conducting clinical research on breast cancer. It allows researchers to identify and select appropriate study participants, compare outcomes across different studies, and draw meaningful conclusions about the disease.
-
Quality improvement initiatives
Coding practices support quality improvement initiatives by providing data that can be used to track and monitor the quality of breast cancer care. This information can help identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance patient outcomes.
The history of breast cancer ICD-10 reflects the evolution of coding practices over time. As our understanding of breast cancer has improved, so too have the coding systems used to classify and describe the disease. This has led to increased accuracy and consistency in coding practices, which has in turn improved the quality of data available for statistical analysis, clinical research, and quality improvement initiatives.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis plays a crucial role in the history of breast cancer ICD-10, providing valuable insights into disease patterns, trends, and outcomes. It utilizes data collected from breast cancer cases to draw meaningful conclusions, inform decision-making, and drive improvements in patient care.
-
Incidence and Prevalence
Statistical analysis allows researchers to determine the incidence (new cases) and prevalence (existing cases) of breast cancer in different populations. This information helps identify populations at higher risk and target prevention and screening efforts.
-
Survival Rates
Statistical analysis is used to calculate survival rates for breast cancer patients. By comparing survival rates over time and across different treatment modalities, researchers can evaluate the effectiveness of various approaches and identify areas for improvement.
-
Prognostic Factors
Statistical analysis helps identify prognostic factors that influence the likelihood of breast cancer recurrence and survival. These factors, such as tumor stage, grade, and molecular subtype, guide treatment decisions and provide valuable information for patients.
-
Quality of Care
Statistical analysis can be used to assess the quality of breast cancer care. By comparing outcomes across different healthcare settings, researchers can identify disparities in care and develop strategies to improve the quality and equity of treatment.
These facets of statistical analysis contribute to our understanding of breast cancer epidemiology, disease progression, and the effectiveness of various treatment approaches. By analyzing data from ICD-10 coded cases, researchers can make informed decisions about resource allocation, public health policies, and future research directions, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for breast cancer patients.
Research Trends
Research trends play a critical role in shaping the history of breast cancer ICD-10. Advances in research have led to a deeper understanding of the disease, its causes, and effective treatments. The evolution of ICD-10 coding reflects the incorporation of new knowledge gained through research into clinical practice.
For instance, the inclusion of molecular subtyping in ICD-10 is a direct result of research findings that identified distinct genetic alterations driving breast cancer development. This refined classification has enabled more personalized treatment approaches, tailoring therapies to the specific molecular characteristics of each tumor.
Research trends also influence the development of new coding guidelines. As research uncovers novel diagnostic techniques or prognostic factors, ICD-10 is updated to incorporate these advancements. This ensures that the coding system remains current with the latest medical knowledge, facilitating accurate data collection and analysis.
Understanding the connection between research trends and the history of breast cancer ICD-10 is crucial for several reasons. It highlights the importance of ongoing research in driving progress against breast cancer. It also emphasizes the need for regular updates to ICD-10 to keep pace with evolving medical knowledge. By leveraging research findings, ICD-10 remains a valuable tool for tracking disease patterns, evaluating treatment outcomes, and informing public health strategies.
Historical Context
Historical context plays a critical role in shaping the history of breast cancer ICD-10. It encompasses the social, cultural, and scientific factors that have influenced our understanding and classification of breast cancer over time. Understanding this context is crucial for interpreting the evolution of ICD-10 coding and its implications for breast cancer diagnosis, treatment, and research.
One key aspect of the historical context is the changing perception of breast cancer as a disease. In the past, breast cancer was often stigmatized and shrouded in secrecy, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. The emergence of public health campaigns and advocacy groups has gradually reduced this stigma, encouraging women to seek regular screenings and medical care.
Another important historical factor is the development of medical technology. Advances in imaging techniques, such as mammography and ultrasound, have significantly improved the early detection of breast cancer. Similarly, the discovery of new genetic markers and molecular subtypes has led to a better understanding of breast cancer biology and the development of targeted therapies.
The history of breast cancer ICD-10 reflects these historical developments, incorporating new knowledge and technologies into its coding system. By understanding the historical context, we can appreciate the evolution of breast cancer classification and its impact on patient care. This understanding can also guide future research and policy decisions aimed at improving breast cancer outcomes.
International Comparisons
International comparisons play a crucial role in the history of breast cancer ICD-10, enabling us to understand variations in breast cancer incidence, mortality, and treatment outcomes across different countries and populations. By examining these differences, we can identify best practices, inform policy decisions, and improve global breast cancer care.
-
Incidence and Mortality Rates
Comparing incidence and mortality rates across countries provides insights into the geographical distribution of breast cancer and its impact on different populations. This information can help identify high-risk areas and target prevention and screening efforts.
-
Treatment Approaches
International comparisons allow us to examine variations in treatment approaches, including surgical techniques, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. This knowledge can inform treatment guidelines and improve the quality of care for breast cancer patients worldwide.
-
Survival Outcomes
Comparing survival outcomes across countries provides valuable information about the effectiveness of different healthcare systems and treatment strategies. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and develop interventions to enhance survival rates.
-
Health Policy and Resource Allocation
International comparisons can inform health policy decisions and resource allocation. By understanding how different countries approach breast cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment, we can identify successful strategies and implement them in other settings.
In conclusion, international comparisons are essential for understanding the global burden of breast cancer and improving patient outcomes. By examining variations in incidence, mortality, treatment approaches, and survival rates across countries, we can identify best practices, inform policy decisions, and ultimately enhance breast cancer care worldwide.
Clinical Implications
The history of breast cancer ICD-10 provides insights into the evolution of clinical practices and their impact on patient outcomes. Clinical implications encompass the practical applications and consequences of advancements in breast cancer classification and management, influencing diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient care.
-
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
The refinement of ICD-10 coding criteria enhances diagnostic accuracy by standardizing the classification of breast cancer subtypes, ensuring consistency in diagnosis and facilitating more precise treatment planning.
-
Personalized Treatment Plans
The incorporation of molecular subtyping into ICD-10 enables personalized treatment approaches tailored to specific tumor characteristics. This allows clinicians to select the most effective therapies for each patient, improving treatment outcomes and reducing unnecessary side effects.
-
Prognostic and Predictive Information
ICD-10 coding provides prognostic and predictive information by categorizing breast cancer based on factors such as tumor stage and grade. This information guides treatment decisions, estimates the likelihood of recurrence, and helps determine the appropriate follow-up care.
-
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
The standardized coding system facilitates effective communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals. It ensures that patient information is accurately and consistently recorded, enabling seamless transitions between different care settings and promoting continuity of care.
In summary, the clinical implications of the history of breast cancer ICD-10 encompass improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment planning, prognostic and predictive information, and enhanced communication and collaboration. These advancements have significantly contributed to the optimization of breast cancer care, leading to better patient outcomes and improved quality of life.
Public Health Significance
The history of breast cancer ICD-10 is intricately connected to its public health significance, as the classification system directly impacts the understanding, prevention, and management of breast cancer in populations.
Accurate and consistent coding of breast cancer cases using ICD-10 enables public health surveillance, allowing for the monitoring of incidence, prevalence, and mortality rates. This information provides valuable insights into the burden of breast cancer in different regions and population groups, guiding resource allocation and public health interventions.
Furthermore, ICD-10 coding facilitates research on breast cancer epidemiology and outcomes. By analyzing large datasets of coded cases, researchers can identify risk factors, evaluate the effectiveness of screening and treatment strategies, and monitor changes in breast cancer patterns over time. This knowledge contributes to the development of evidence-based public health policies and programs aimed at reducing breast cancer morbidity and mortality.
In summary, the history of breast cancer ICD-10 is inseparable from its public health significance. The standardized coding system enables effective surveillance, research, and public health interventions, ultimately contributing to the improvement of breast cancer outcomes and the well-being of populations.
Frequently Asked Questions on the History of Breast Cancer ICD-10
This FAQ section addresses common questions and clarifies key aspects related to the history of breast cancer ICD-10. It provides concise answers to anticipated reader queries, offering a deeper understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What is the significance of ICD-10 in breast cancer classification?
Answer: ICD-10 plays a crucial role in standardizing the classification and coding of breast cancer cases, ensuring consistent and accurate disease identification and management across healthcare settings.
Question 2: How has ICD-10 evolved over time to reflect advances in breast cancer understanding?
Answer: ICD-10 has undergone regular revisions to incorporate new knowledge and advancements in breast cancer diagnosis, treatment, and research. This evolution ensures that the coding system remains current with the latest medical understanding and clinical practices.
Question 3: What are the benefits of using ICD-10 for breast cancer research?
Answer: ICD-10 provides a standardized framework for data collection and analysis in breast cancer research. It enables researchers to compare results across studies, identify trends, and draw meaningful conclusions about breast cancer epidemiology, risk factors, and treatment outcomes.
Question 4: How does ICD-10 impact public health strategies for breast cancer?
Answer: ICD-10 coding facilitates accurate breast cancer surveillance and monitoring. It provides data for public health agencies to develop targeted prevention programs, screening guidelines, and treatment policies aimed at reducing breast cancer burden and improving patient outcomes.
Question 5: What are the challenges associated with the use of ICD-10 for breast cancer coding?
Answer: Challenges include ensuring accurate and consistent coding practices among healthcare providers, addressing potential coding errors, and keeping up with the evolving ICD-10 coding guidelines to reflect advancements in breast cancer knowledge.
Question 6: What future developments can we expect in ICD-10 coding for breast cancer?
Answer: As breast cancer research continues to uncover new insights and technologies emerge, we can anticipate further revisions to ICD-10 to incorporate these advancements and enhance the precision and utility of breast cancer classification.
These FAQs provide a glimpse into the history of breast cancer ICD-10, its significance, benefits, and challenges. Understanding these aspects is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of breast cancer classification and its implications for diagnosis, treatment, and public health.
This discussion sets the stage for further exploration of the topic, delving into specific historical milestones, key individuals, and the impact of ICD-10 on breast cancer management.
Tips for Navigating the History of Breast Cancer ICD-10
Understanding the history of breast cancer ICD-10 is a valuable endeavor for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of breast cancer classification and its implications. Here are five tips to effectively navigate this topic:
Tip 1: Explore Historical Context: Understand the social, cultural, and scientific factors that shaped the evolution of ICD-10 coding for breast cancer.
Tip 2: Trace Diagnostic Criteria Changes: Examine how diagnostic criteria for breast cancer have evolved over time, influencing disease identification and management.
Tip 3: Analyze Treatment Approach Developments: Identify key advancements in breast cancer treatment modalities, such as surgical techniques, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies, as reflected in ICD-10 coding.
Tip 4: Examine Coding Practice Evolution: Investigate the standardization and refinement of coding practices for breast cancer, ensuring accuracy and consistency in data collection.
Tip 5: Utilize Research Trends for Insights: Explore how research findings have influenced the incorporation of new knowledge and technologies into ICD-10 coding for breast cancer.
These tips provide a framework for delving into the history of breast cancer ICD-10, enabling a comprehensive understanding of its evolution and significance in breast cancer management.
Understanding these historical developments lays the groundwork for appreciating the current state of breast cancer classification and its implications for clinical practice, research, and public health initiatives.
Conclusion
Throughout history, the classification of breast cancer using ICD-10 has undergone significant evolution, reflecting advancements in medical understanding and clinical practices. This refined classification has enabled more accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment planning, improved prognostic information, and enhanced communication among healthcare professionals.
The key insights gained from exploring the history of breast cancer ICD-10 include the evolving diagnostic criteria, the development of new treatment approaches, and the increasing importance of international comparisons and public health implications. These historical developments have shaped our current understanding and management of breast cancer, leading to improved outcomes for patients.