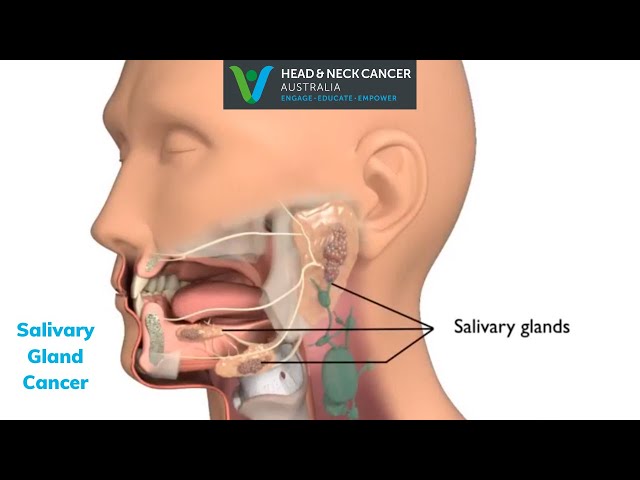
Salivary gland cancer symptoms are physical signs or sensations that indicate a problem with the salivary glands, which produce saliva to aid in digestion and oral hygiene. One common symptom is the presence of a lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck.
Detecting salivary gland cancer symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, as the cancer can spread to other parts of the head and neck. Early identification can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and prevent complications.
This article will delve into the various symptoms of salivary gland cancer, their causes, and the importance of prompt medical attention. It will also provide information on risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options.
salivary gland cancer symptoms
Salivary gland cancer symptoms are critical indicators of a potential underlying medical condition, necessitating prompt attention and proper diagnosis. Understanding these symptoms empowers individuals to recognize the warning signs and seek timely medical intervention, leading to improved treatment outcomes.
- Lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Facial numbness or weakness
- Changes in voice or speech
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unexplained bleeding from the mouth
- Persistent bad breath
These symptoms can vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. Recognizing any of these signs should trigger immediate consultation with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early identification and treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes, including the preservation of salivary gland function and overall quality of life.
Lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck
A lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer, indicating the presence of abnormal tissue growth within the salivary glands. It is essential to recognize this symptom and seek prompt medical attention, as timely diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
- Location: The lump or swelling can occur in various locations, including the parotid glands (located below and in front of the ears), submandibular glands (located under the jawbone), and sublingual glands (located under the tongue).
- Size and shape: The size and shape of the lump or swelling can vary, ranging from small and round to large and irregular. It may be firm or soft to the touch and may cause pain or discomfort.
- Accompanying symptoms: In some cases, a lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as facial numbness or weakness, difficulty opening the mouth, or changes in voice or speech.
- Progression: If left untreated, the lump or swelling may gradually increase in size and spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. It is important to monitor any changes in the lump or swelling and report them to a healthcare professional promptly.
Understanding the various aspects of a lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck in relation to salivary gland cancer symptoms is crucial. Early detection and proper diagnosis can lead to timely intervention and improve the chances of successful treatment, preserving salivary gland function and overall quality of life.
Pain or tenderness in the affected area
Pain or tenderness in the affected area is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer, occurring when the cancerous growth exerts pressure on nearby nerves or tissues. It can manifest in various forms, providing valuable clues for early detection and diagnosis.
- Location: Pain or tenderness associated with salivary gland cancer is typically localized to the area of the affected gland, such as the parotid glands, submandibular glands, or sublingual glands.
- Intensity: The intensity of pain or tenderness can range from mild discomfort to severe, throbbing pain. It may be constant or intermittent, and its severity can fluctuate over time.
- Aggravating factors: In some cases, pain or tenderness may be aggravated by certain activities, such as eating, speaking, or opening the mouth wide.
- Radiation: In advanced stages of salivary gland cancer, pain or tenderness may radiate to other areas of the head and neck, including the ears, jaw, or neck.
Understanding the characteristics and implications of pain or tenderness in the affected area is essential for recognizing salivary gland cancer symptoms and seeking timely medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and preserve salivary gland function. If you experience persistent or worsening pain or tenderness in the cheek, jaw, or neck, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Difficulty opening the mouth
Difficulty opening the mouth, medically termed trismus, is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer, arising due to the growth and spread of cancerous cells within or around the salivary glands.
As the tumor enlarges, it can impinge on the surrounding tissues and nerves, causing inflammation and fibrosis, which restrict the movement of the jaw muscles. This leads to difficulty in opening the mouth, making it challenging to perform everyday activities such as eating, speaking, and maintaining oral hygiene.
The severity of trismus can vary depending on the location and stage of the salivary gland cancer. In some cases, difficulty opening the mouth may be the initial presenting symptom, while in others, it may develop gradually as the cancer progresses.
Recognizing difficulty opening the mouth as a potential symptom of salivary gland cancer is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent further impairment of jaw function and improve the chances of successful treatment outcomes. Healthcare professionals may recommend various interventions, including physical therapy, surgery, or radiation therapy, to address trismus and restore jaw mobility.
Facial numbness or weakness
Facial numbness or weakness is a symptom of salivary gland cancer that arises due to the involvement of nerves that control facial movements. It can manifest in various forms and provides valuable clues for early detection and diagnosis.
- Paralysis: Complete loss of movement in a specific area of the face.
- Paresthesia: Abnormal sensations, such as tingling, prickling, or burning, in a specific area of the face.
- Drooping: Inability to control the muscles on one side of the face, leading to a drooping appearance.
- Asymmetry: Noticeable difference in facial appearance between the affected and unaffected sides.
Facial numbness or weakness in the context of salivary gland cancer symptoms can indicate the spread of the cancer to nearby nerves or tissues. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms and seek timely medical attention, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further complications. Healthcare professionals will assess the extent of facial numbness or weakness and recommend appropriate interventions, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or physical therapy, to restore facial function and improve overall quality of life.
Changes in voice or speech
Changes in voice or speech are common symptoms of salivary gland cancer, occurring when the cancerous growth affects the nerves or muscles involved in speech production. These changes can range from subtle alterations in voice quality to complete loss of speech, depending on the location and extent of the cancer.
One of the main causes of voice changes in salivary gland cancer is the involvement of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which controls the movement of the vocal cords. When the cancer affects this nerve, it can lead to hoarseness, breathiness, or difficulty speaking. In severe cases, it can cause complete paralysis of the vocal cords, resulting in aphonia (loss of voice).
Changes in speech can also occur due to the enlargement of the salivary gland tumor, which can obstruct the oral cavity and pharynx, making it difficult to articulate words clearly. Additionally, the presence of a tumor in the mouth or throat can interfere with the movement of the tongue and palate, further affecting speech production.
Recognizing changes in voice or speech as potential symptoms of salivary gland cancer is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare professionals will assess the nature and severity of these changes and recommend appropriate interventions, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or speech therapy, to restore speech function and improve overall quality of life.
Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing, medically known as dysphagia, is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer, occurring when the cancerous growth obstructs or impairs the passage of food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
Salivary gland cancer can cause difficulty swallowing in several ways. The tumor can directly obstruct the oral cavity or pharynx, making it challenging to initiate swallowing. Additionally, the cancer can involve the nerves or muscles involved in swallowing, leading to incoordination and impaired movement of the muscles responsible for this process.
In some cases, difficulty swallowing may be the initial presenting symptom of salivary gland cancer, while in others, it may develop gradually as the cancer progresses. It is important to recognize difficulty swallowing as a potential symptom of salivary gland cancer and seek timely medical attention, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
Healthcare professionals will assess the nature and severity of difficulty swallowing and recommend appropriate interventions, which may include dietary modifications, speech therapy, or surgery, to improve swallowing function and enhance overall quality of life.
Unexplained bleeding from the mouth
Unexplained bleeding from the mouth is a symptom of salivary gland cancer that arises due to the growth and involvement of the tumor within the salivary glands or surrounding tissues. The cancerous growth can erode blood vessels, leading to bleeding that may manifest as blood in the saliva, coughing up blood, or unexplained bleeding from the mouth.
Unexplained bleeding from the mouth is not a common initial symptom of salivary gland cancer and is more likely to occur in advanced stages of the disease. It is important to recognize this symptom and seek timely medical attention, as it can indicate the spread of the cancer to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
Healthcare professionals will assess the nature and severity of unexplained bleeding from the mouth and recommend appropriate interventions, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or embolization, to control the bleeding and address the underlying salivary gland cancer.
Understanding the connection between unexplained bleeding from the mouth and salivary gland cancer symptoms is crucial for early detection, diagnosis, and timely treatment. By recognizing this symptom and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can improve their chances of successful treatment outcomes and preserve their overall quality of life.
Persistent bad breath
Persistent bad breath, medically known as halitosis, is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer that arises due to the disruption of the normal oral environment and the growth of the cancerous tumor within the salivary glands.
Salivary glands play a crucial role in maintaining oral hygiene by producing saliva, which helps wash away bacteria and food particles that can cause bad breath. When salivary gland cancer develops, it can obstruct the production and flow of saliva, leading to a buildup of bacteria and an increase in the levels of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), which are responsible for the unpleasant odor associated with halitosis.
In addition, salivary gland cancer can cause other symptoms that contribute to bad breath, such as bleeding from the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and oral pain. These symptoms can further impair oral hygiene practices, creating a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria and the development of halitosis.
Recognizing persistent bad breath as a potential symptom of salivary gland cancer is crucial for early detection and diagnosis. While halitosis can be caused by various factors, its presence in combination with other salivary gland cancer symptoms should prompt individuals to seek timely medical attention. Healthcare professionals will assess the nature and severity of halitosis and perform a thorough examination to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Salivary Gland Cancer Symptoms
This FAQ section provides concise answers to common questions and concerns regarding the symptoms of salivary gland cancer. These questions aim to clarify various aspects of the condition and help individuals better understand its presentation.
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of salivary gland cancer?
Answer: The most common symptoms include a lump or swelling in the cheek, jaw, or neck; pain or tenderness in the affected area; difficulty opening the mouth; facial numbness or weakness; changes in voice or speech; difficulty swallowing; unexplained bleeding from the mouth; and persistent bad breath.
Question 2: Can salivary gland cancer cause pain?
Answer: Yes, pain or tenderness in the affected area is a common symptom of salivary gland cancer, especially as the tumor grows and exerts pressure on nearby nerves and tissues.
Question 3: How does salivary gland cancer affect speech?
Answer: Salivary gland cancer can cause changes in voice or speech if it affects the nerves or muscles involved in speech production, leading to hoarseness, breathiness, difficulty speaking, or even complete loss of voice.
Question 4: Can salivary gland cancer make it difficult to swallow?
Answer: Yes, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can occur if the salivary gland tumor obstructs the oral cavity or pharynx or involves the nerves or muscles responsible for swallowing.
Question 5: What should I do if I experience any of these symptoms?
Answer: It is important to seek timely medical attention if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for salivary gland cancer.
Question 6: Are there any other symptoms associated with salivary gland cancer?
Answer: In addition to the common symptoms, salivary gland cancer can also cause facial numbness or weakness, unexplained bleeding from the mouth, and persistent bad breath.
In summary, salivary gland cancer can manifest through various symptoms, including a lump or swelling, pain, difficulty opening the mouth, facial numbness, speech changes, swallowing difficulties, bleeding, and bad breath. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The next section of this article will delve deeper into the causes and risk factors associated with salivary gland cancer, providing further insights into the development and progression of this condition.
Tips for Managing Salivary Gland Cancer Symptoms
Managing the symptoms of salivary gland cancer can help improve overall comfort and quality of life during treatment. Here are some practical tips to consider:
Tip 1: Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth and floss regularly to maintain oral health and prevent infections.
Tip 2: Use a soft toothbrush: Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating sensitive tissues.
Tip 3: Use a mouth rinse: Use a gentle mouth rinse to keep your mouth clean and refreshed.
Tip 4: Apply cold compresses: Applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling.
Tip 5: Elevate your head while sleeping: Elevating your head while sleeping can help reduce swelling and improve drainage.
Tip 6: Eat a soft diet: Stick to soft, easy-to-chew foods to avoid discomfort while eating.
Tip 7: Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your mouth moist and prevent dryness.
Tip 8: Avoid tobacco and alcohol: Smoking and drinking alcohol can irritate the mouth and worsen symptoms.
Following these tips can help alleviate salivary gland cancer symptoms and improve your overall well-being. It is important to remember that every individual's experience is unique, and consulting with your healthcare team for personalized advice is always recommended.
The next section of this article will discuss the importance of regular follow-up care after salivary gland cancer treatment, emphasizing the role of monitoring and surveillance in long-term management.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding salivary gland cancer symptoms is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Recognizing the various symptoms, such as lumps or swellings, pain, difficulty opening the mouth, facial numbness, speech changes, and unexplained bleeding, empowers individuals to seek prompt medical attention.
Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve outcomes, preserve salivary gland function, and enhance overall quality of life. This article has highlighted the importance of recognizing and managing salivary gland cancer symptoms, emphasizing the need for ongoing monitoring and follow-up care to ensure the best possible outcomes for patients.