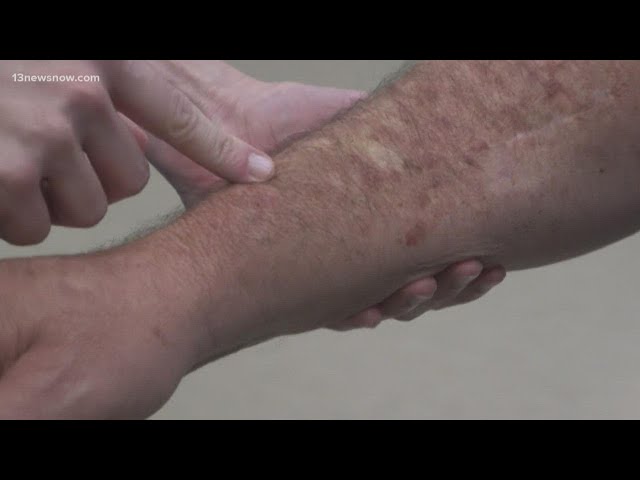
A skin cancer rash is a common and potentially serious condition that can develop when skin cells are damaged by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources. The rash can appear as a variety of skin changes, including red or white patches, scaling, and thickening.
Skin cancer rash is a major public health concern, as it is the most common type of cancer in the United States. The rash can lead to serious health complications if not diagnosed and treated early. Early detection and treatment of skin cancer rash is essential to prevent the development of more serious skin cancer.
In the past, skin cancer rash was often misdiagnosed as other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis. However, today there are a number of effective methods for diagnosing and treating skin cancer rash, including biopsy, surgery, and radiation therapy.
Skin Cancer Rash
Skin cancer rash is a common and potentially serious condition that can develop when skin cells are damaged by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources. The rash can appear as a variety of skin changes, including red or white patches, scaling, and thickening.
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Risk Factors
- Complications
- Prognosis
- Outlook
These key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of skin cancer rash, covering its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, risk factors, complications, prognosis, and outlook. By understanding these aspects, individuals can be better informed about this condition and take steps to protect themselves from developing it.
Symptoms
Symptoms are an essential component of skin cancer rash, as they provide valuable clues for diagnosis and treatment. The most common symptom of skin cancer rash is a change in the skin's appearance, such as a new mole, a change in the size or shape of an existing mole, or a sore that does not heal. Other symptoms may include itching, bleeding, or crusting.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of skin cancer rash, as early detection and treatment can improve the chances of a successful outcome. If you notice any changes in your skin, it is important to see a doctor right away for evaluation.
By understanding the symptoms of skin cancer rash, individuals can be more proactive in protecting their skin from the sun's harmful UV rays. This includes wearing sunscreen, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and avoiding tanning beds.
Causes
The primary cause of skin cancer rash is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources, such as tanning beds. UV radiation can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to the development of skin cancer. The amount of UV radiation exposure a person receives depends on several factors, including the time of day, the season, the geographic location, and the amount of skin that is exposed.
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing skin cancer rash than others. These individuals include those with fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, a weakened immune system, and those who have had extensive sun exposure. Additionally, certain occupations and activities can increase the risk of developing skin cancer rash, such as working outdoors or participating in outdoor sports.
Understanding the causes of skin cancer rash is critical for prevention. By taking steps to protect the skin from UV radiation, such as wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and avoiding tanning beds, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this condition.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis plays a pivotal role in skin cancer rash, as it allows healthcare professionals to accurately identify and distinguish it from other skin conditions. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan and improving the chances of a successful outcome.
The diagnosis of skin cancer rash typically involves a physical examination of the affected area, a review of the patient's medical history, and sometimes a biopsy. During the physical examination, the doctor will assess the size, shape, color, and texture of the rash. They will also inquire about any associated symptoms, such as itching, bleeding, or pain.
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of skin cancer rash. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of the affected skin and examining it under a microscope. This procedure allows the doctor to determine the type of skin cancer and its stage.
Early and accurate diagnosis of skin cancer rash is essential for effective treatment and improved outcomes. By understanding the connection between diagnosis and skin cancer rash, individuals can be more proactive in seeking medical attention if they notice any suspicious changes in their skin.
Treatment
Treatment plays a pivotal role in the management of skin cancer rash, aiming to eliminate the cancerous cells and prevent the spread of the disease. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the type and stage of skin cancer, the patient's overall health, and their preferences.
Various treatment options are available for skin cancer rash, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Surgery is the most common treatment for skin cancer rash and involves removing the cancerous tissue. Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells, while chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body. Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells, leaving healthy cells unharmed.
Understanding the connection between treatment and skin cancer rash empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. By seeking timely and appropriate treatment, patients can improve their chances of a successful outcome and prevent the progression of the disease. Moreover, ongoing research and advancements in treatment modalities offer hope for even more effective and personalized approaches in the future.
Prevention
Prevention is a crucial aspect of skin cancer rash management, as it aims to reduce the risk of developing this condition in the first place. Several preventive measures can be taken to protect the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, the primary cause of skin cancer rash.
-
Sun Protection
Using sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher and reapplying it every two hours is essential for protecting the skin from UV radiation. Additionally, wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats, can provide further protection.
-
Sun Avoidance
Avoiding excessive sun exposure, especially during peak hours between 10 am and 4 pm, is crucial. Seeking shade under umbrellas, trees, or other structures can help minimize UV exposure.
-
Tanning Avoidance
Artificial tanning, whether through tanning beds or sunlamps, should be avoided as it emits high levels of UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
-
Regular Skin Exams
Regularly examining the skin for any changes in size, shape, or color of moles or other skin lesions is important for early detection of skin cancer. Self-exams can be performed monthly, and professional skin exams by a dermatologist are recommended annually.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin cancer rash. Sun protection, sun avoidance, tanning avoidance, and regular skin exams are key components of a comprehensive prevention strategy. Early detection through regular skin exams can improve the chances of successful treatment and prevent the progression of skin cancer.
Risk Factors
Risk factors are characteristics or exposures that increase the probability of developing a disease or condition, such as skin cancer rash. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health.
-
Fair Skin
Individuals with fair skin are more susceptible to sun damage and skin cancer, as they have less melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation.
-
Family History
A family history of skin cancer increases the risk of developing the condition, as certain genes can be inherited that make individuals more prone to developing skin cancer.
-
Sun Exposure
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the primary risk factor for skin cancer rash. UV radiation can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to the development of skin cancer.
-
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with a weakened immune system are more susceptible to developing skin cancer, as their immune system is less able to fight off damaged skin cells.
By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing skin cancer rash. These steps include protecting the skin from sun exposure, avoiding tanning beds, and getting regular skin exams. Early detection and treatment of skin cancer rash can improve the chances of a successful outcome.
Complications
Complications related to skin cancer rash can arise if the condition is left untreated or progresses to more advanced stages. These complications can range from localized skin damage to more serious systemic issues, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention.
-
Infection
Open sores and lesions caused by skin cancer rash can become infected, leading to pain, swelling, and fever. In severe cases, the infection may spread to the bloodstream or other parts of the body.
-
Scarring
Healing skin cancer rash can result in scarring, especially if the rash is deep or extensive. Scarring can cause disfigurement, loss of function, and psychological distress.
-
Skin Damage
Skin cancer rash can cause significant damage to the skin, leading to dryness, cracking, and loss of elasticity. This damage can make the skin more susceptible to further infections and other complications.
-
Metastasis
In advanced stages, skin cancer rash can spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes and internal organs. Metastasis can be life-threatening and requires aggressive treatment.
Understanding the potential complications associated with skin cancer rash underscores the need for prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent or minimize these adverse outcomes. Regular skin self-exams, sun protection measures, and seeking medical attention for any suspicious skin changes are crucial for maintaining skin health and overall well-being.
Prognosis
Prognosis in skin cancer rash refers to the predicted course and outcome of the condition. It is influenced by various factors and can provide valuable insights for treatment planning and patient management.
-
Stage of Rash
The stage of the rash, whether early or advanced, significantly affects the prognosis. Early-stage rashes are more likely to respond well to treatment and have a better prognosis compared to advanced-stage rashes that may have spread or become more aggressive.
-
Type of Rash
Different types of skin cancer rashes have varying prognoses. Some rashes may be more aggressive and require more extensive treatment, while others may be less severe and have a more favorable prognosis.
-
Patient's Health
The overall health of the patient, including their immune system and presence of any underlying medical conditions, can impact the prognosis. Patients with a weakened immune system or other health issues may have a less favorable prognosis.
-
Treatment Response
The response to treatment is a crucial factor in determining the prognosis. Rashes that respond well to treatment and show signs of improvement have a better prognosis compared to those that do not respond as effectively.
Understanding the prognosis of skin cancer rash allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about treatment options, provide patients with realistic expectations, and develop appropriate follow-up plans. By considering the stage of the rash, type of rash, patient's health, and treatment response, a more accurate assessment of the prognosis can be made, leading to better patient care and outcomes.
Outlook
The outlook for skin cancer rash depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the rash, the patient's overall health, and the response to treatment. Understanding the outlook can help patients make informed decisions about their care and prepare for the future.
-
Treatment Outcome
The success of treatment plays a significant role in determining the outlook. Rashes that respond well to treatment and show signs of improvement have a better outlook compared to those that do not respond as effectively.
-
Recurrence Risk
Some types of skin cancer rashes have a higher risk of recurrence, even after successful treatment. Patients with a history of skin cancer rash should be monitored closely for any signs of recurrence.
-
Quality of Life
Skin cancer rash can impact the quality of life, both physically and emotionally. The rash can cause pain, itching, and disfigurement, which can affect a person's self-esteem and social interactions.
-
Long-Term Effects
In some cases, skin cancer rash can lead to long-term effects, such as scarring or damage to the skin. These effects can be permanent and may require ongoing management.
The outlook for skin cancer rash is generally good if it is detected and treated early. However, the specific outlook depends on the individual circumstances of each patient. By understanding the potential outcomes and implications, patients can work with their healthcare providers to develop an appropriate treatment plan and manage their condition effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skin Cancer Rash
The following FAQs provide answers to some of the most common questions and concerns regarding skin cancer rash, helping individuals better understand the condition, its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of skin cancer rash?
Answer: Common symptoms include red or white patches on the skin, scaling, thickening, itching, bleeding, or crusting.
Question 2: What causes skin cancer rash?
Answer: Skin cancer rash is primarily caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources, such as tanning beds.
Question 3: How is skin cancer rash diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, a review of medical history, and sometimes a biopsy to examine a sample of the affected skin under a microscope.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for skin cancer rash?
Answer: Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, with the choice of treatment depending on factors such as the type and stage of the rash.
Question 5: How can I prevent skin cancer rash?
Answer: Prevention measures include sun protection (using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade), sun avoidance (limiting exposure during peak hours), avoiding tanning, and getting regular skin exams.
Question 6: What is the prognosis for skin cancer rash?
Answer: The prognosis depends on factors such as the stage and type of rash, the patient's overall health, and the response to treatment. Early detection and appropriate treatment generally lead to a good prognosis.
These FAQs provide a concise overview of essential information regarding skin cancer rash. For further insights and a more comprehensive understanding of the condition, its management, and implications, please continue reading the full article.
(Transition to the next section: Understanding the Types of Skin Cancer Rash)
Tips for Preventing Skin Cancer Rash
Understanding the causes and risk factors of skin cancer rash is crucial, but taking proactive steps to prevent its occurrence is equally important. Here are several practical and actionable tips to help reduce your risk and maintain healthy skin:
Tip 1: Seek Shade and Cover Up: Limit your exposure to the sun's harmful UV rays, especially during peak hours. Seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures, and wear protective clothing such as long sleeves, pants, and hats.
Tip 2: Use Sunscreen Regularly: Apply sunscreen generously to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
Tip 3: Avoid Tanning: Avoid artificial tanning through tanning beds or sunlamps, as they emit high levels of UV radiation that can damage the skin.
Tip 4: Wear Protective Eyewear: Protect your eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses that block 99-100% of UVA and UVB rays.
Tip 5: Examine Your Skin Regularly: Perform regular self-exams of your skin, checking for any changes in size, shape, or color of moles or other skin lesions. Report any suspicious changes to a dermatologist promptly.
Tip 6: Be Sun-Smart in All Seasons: Sun protection is not just for summer. Even during winter or on overcast days, UV rays can still penetrate the skin. Take precautions year-round to safeguard your skin.
Tip 7: Protect Children: Children's skin is more vulnerable to sun damage. Implement sun protection measures for children, including sunscreen, protective clothing, and limiting their time in direct sunlight.
Tip 8: Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Some skin care products and fragrances can increase the skin's sensitivity to UV radiation. Choose skincare products that are gentle and non-irritating.
By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer rash and maintain healthier skin overall.
(Transition to the article's conclusion: Remember, prevention is key in safeguarding your skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By adopting these simple yet effective measures, you can protect your skin's health and well-being for years to come.)
Conclusion
Understanding skin cancer rash is essential for individuals to safeguard their skin health. By recognizing its causes, risk factors, and symptoms, we can take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome.
Key takeaways include:
- Sun exposure is the primary cause of skin cancer rash, and preventive measures such as sunscreen, protective clothing, and shade-seeking are crucial.
- Individuals with fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, or a weakened immune system are at higher risk and should be particularly vigilant in sun protection.
- Regular skin self-exams and professional skin exams are vital for early detection and timely intervention.
Remember, skin cancer rash is a preventable and treatable condition when detected early. By embracing sun-safe practices and maintaining good skin care habits, we can protect our skin's health and well-being for years to come.