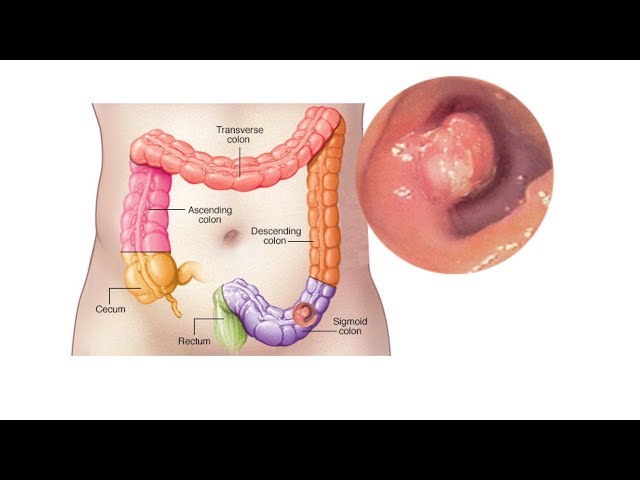
Symptoms of colon cancer are physical indications or experiences that suggest the presence of cancer in the large intestine. For instance, persistent abdominal pain, blood in stools, and unexplained weight loss may be telltale signs.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment, potentially improving chances of successful outcomes. Historically, advances in medical imaging, such as colonoscopies, have played a pivotal role in identifying colon cancer at earlier stages.
This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into the various symptoms associated with colon cancer, their significance, and the importance of timely medical intervention to optimize patient outcomes.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Understanding the symptoms of colon cancer is vital for early detection and effective treatment. These symptoms provide crucial insights into the presence and progression of the disease.
- Abdominal pain
- Rectal bleeding
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
These symptoms can vary in severity and may not always indicate colon cancer. However, it is essential to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms persist or worsen. Early detection can lead to more successful treatment outcomes.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common and often debilitating symptom of colon cancer. It occurs when a tumor obstructs the colon, causing pressure and inflammation. The pain can be sharp, dull, or crampy, and it may be localized to one area of the abdomen or more widespread.
Abdominal pain is a critical component of colon cancer symptoms because it can indicate the presence of a tumor. In many cases, abdominal pain is the first symptom that prompts individuals to seek medical attention. Early detection and treatment of colon cancer is essential for improving patient outcomes, and abdominal pain plays a vital role in facilitating this process.
For instance, a 55-year-old patient with persistent abdominal pain and changes in bowel habits underwent a colonoscopy, which revealed a cancerous tumor in the sigmoid colon. The early detection of the tumor, prompted by the abdominal pain, allowed for timely surgical intervention and a favorable prognosis.
Understanding the connection between abdominal pain and colon cancer enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing abdominal pain as a potential indicator of colon cancer, clinicians can prioritize further investigation and appropriate interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Rectal bleeding
Rectal bleeding, also known as hematochezia, is a common and often alarming symptom of colon cancer. It occurs when blood from the colon or rectum is passed during bowel movements. The blood may be bright red, dark red, or maroon in color, and it may be mixed with stool or appear on its own.
Rectal bleeding is a critical component of colon cancer symptoms because it can indicate the presence of a tumor or other abnormalities in the colon or rectum. When a tumor bleeds, it can cause blood to mix with stool, resulting in visible rectal bleeding. In some cases, rectal bleeding may be the first and only symptom of colon cancer, making it essential to seek medical attention promptly if this symptom is noticed.
For instance, a 62-year-old patient experienced persistent rectal bleeding and changes in bowel habits. A colonoscopy revealed a cancerous tumor in the descending colon. The early detection of the tumor, prompted by the rectal bleeding, allowed for timely surgical intervention and a favorable prognosis.
Understanding the connection between rectal bleeding and colon cancer enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing rectal bleeding as a potential indicator of colon cancer, clinicians can prioritize further investigation and appropriate interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Constipation
Constipation is a common symptom of colon cancer, characterized by infrequent or difficult bowel movements. It occurs when stool becomes hard and dry, making it challenging to pass. Constipation can be a sign of a blockage or narrowing in the colon, which may be caused by a tumor or other abnormalities.
-
Delayed Passage
Constipation in colon cancer often involves delayed passage of stool through the colon. The tumor can obstruct the colon, slowing down the movement of stool and leading to constipation. -
Straining
Constipation can cause straining during bowel movements as the hard and dry stool requires more effort to pass. Excessive straining can lead to hemorrhoids or anal fissures. -
Incomplete Evacuation
Individuals with constipation may feel like they cannot fully empty their bowels, leading to a sense of incomplete evacuation. This can be caused by the blockage or narrowing in the colon, preventing stool from passing through easily. -
Abdominal Discomfort
Constipation can lead to abdominal discomfort, bloating, and gas. The retained stool can put pressure on the colon, causing pain and discomfort.
Constipation, along with other symptoms such as abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and unexplained weight loss, can be an indication of colon cancer. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if constipation persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early detection and treatment of colon cancer can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, characterized by loose and frequent bowel movements, is a common symptom of colon cancer. It occurs when the colon becomes irritated and inflamed, leading to changes in stool consistency and frequency.
-
Increased Frequency
Diarrhea in colon cancer often involves an increased frequency of bowel movements, with stools being passed more often than usual.
-
Loose and Watery
Diarrheal stools in colon cancer tend to be loose and watery, lacking the usual solid form. This is due to the increased fluid content in the stool.
-
Urgency
Individuals with colon cancer may experience a sense of urgency to pass stool, leading to difficulty controlling bowel movements.
-
Incontinence
Severe diarrhea in colon cancer can sometimes lead to incontinence, resulting in an involuntary loss of stool.
Diarrhea, along with other symptoms such as abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and unexplained weight loss, can be an indication of colon cancer. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if diarrhea persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early detection and treatment of colon cancer can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Unexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a common and concerning symptom of colon cancer, often indicating advanced stages of the disease. It occurs when the body's metabolism is disrupted due to the presence of cancer, leading to a decrease in appetite and an increase in energy expenditure.
-
Reduced Appetite
Tumors can release substances that affect appetite-regulating hormones, leading to a decreased desire to eat and reduced food intake.
-
Malabsorption
Colon cancer can damage the colon's ability to absorb nutrients from food, resulting in weight loss despite adequate food intake.
-
Increased Metabolic Rate
Cancer cells have a high metabolic rate, consuming energy and contributing to weight loss.
-
Cachexia
In advanced stages of colon cancer, the body enters a state of cachexia, characterized by muscle wasting and weight loss.
Unexplained weight loss, along with other symptoms such as abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and diarrhea, can be an indication of colon cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if weight loss occurs without an apparent cause or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early detection and treatment of colon cancer can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a debilitating symptom of colon cancer, encompassing a profound sense of tiredness and exhaustion that extends beyond typical feelings of weariness. This fatigue is often persistent and unresponsive to rest or sleep, significantly affecting daily life and overall well-being.
-
Physical Exhaustion
Colon cancer can lead to physical exhaustion, making even simple tasks feel overwhelming. Patients may experience a lack of energy and an inability to sustain physical activities.
-
Cognitive Impairment
Fatigue associated with colon cancer can impair cognitive function, affecting concentration, memory, and decision-making abilities. This can disrupt daily routines and social interactions.
-
Emotional Distress
The fatigue of colon cancer often goes hand-in-hand with emotional distress, such as anxiety, depression, and irritability. This can further worsen the patient's overall well-being and quality of life.
-
Reduced Quality of Life
Fatigue can significantly diminish a patient's quality of life, hindering their ability to engage in meaningful activities, work, and maintain relationships.
These facets of fatigue underscore its multifaceted impact on individuals with colon cancer. By understanding and addressing fatigue, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Nausea
Nausea is a common and distressing symptom of colon cancer, characterized by a feeling of queasiness and an urge to vomit. It can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and overall well-being.
-
Physical Discomfort
Nausea can cause physical discomfort, including stomach upset, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. These symptoms can interfere with daily activities and make it difficult to maintain a healthy diet.
-
Emotional Distress
Nausea can also lead to emotional distress, anxiety, and depression. The constant feeling of queasiness can disrupt sleep, impair concentration, and affect mood.
-
Dehydration
Persistent nausea can lead to dehydration, as the body is unable to retain fluids. Dehydration can further worsen fatigue and other symptoms of colon cancer.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nausea can interfere with food intake, leading to nutritional deficiencies. This can weaken the immune system and make the body more susceptible to infections.
These facets of nausea highlight its multidimensional impact on individuals with colon cancer. Nausea not only causes physical discomfort but also affects emotional well-being, hydration status, and nutritional intake. By understanding and addressing nausea, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Vomiting
Vomiting, the forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth, is a common symptom of colon cancer, particularly in advanced stages. It occurs when the tumor obstructs the colon, hindering the normal passage of food and fluids. The obstruction can lead to nausea, abdominal discomfort, and eventually vomiting.
Vomiting can be a critical component of colon cancer symptoms, as it can indicate a blockage or other complications. Persistent and severe vomiting can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and nutritional deficiencies. These effects can further weaken the body and compromise overall health, making it crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
For instance, a 72-year-old patient with a history of colon polyps experienced persistent vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation. A colonoscopy revealed an obstructing tumor in the sigmoid colon. The vomiting, in this case, was a crucial symptom that prompted further investigation and led to a timely diagnosis and surgical intervention.
Understanding the connection between vomiting and colon cancer enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing vomiting as a potential indicator of colon cancer, clinicians can prioritize further investigation and appropriate interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Timely management of vomiting and its underlying causes, including adequate hydration and nutritional support, can help alleviate discomfort and improve the patient's overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Colon Cancer Symptoms
This section addresses common questions and concerns regarding colon cancer symptoms, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the most common symptoms of colon cancer?
Answer: The most prevalent symptoms include abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, constipation, diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.
Question 2: Can colon cancer symptoms appear gradually or suddenly?
Answer: Symptoms often develop gradually over time, but they can sometimes appear more suddenly, especially in advanced stages of the disease.
Question 3: Is it possible to have colon cancer without experiencing any symptoms?
Answer: In the early stages, colon cancer may not produce noticeable symptoms. Regular screening is crucial for early detection even in the absence of symptoms.
Question 4: How are colon cancer symptoms diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, blood tests, stool tests, and imaging procedures such as colonoscopy.
Question 5: Can certain factors increase the risk of colon cancer symptoms?
Answer: Age, family history, certain dietary choices, smoking, and obesity can elevate the risk of developing colon cancer and its associated symptoms.
Question 6: What should I do if I experience potential colon cancer symptoms?
Answer: It is vital to seek medical attention promptly if you experience persistent or concerning symptoms, such as abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or unexplained weight loss.
These FAQs provide a concise overview of colon cancer symptoms, emphasizing the importance of early detection and timely intervention. The following section delves into the significance of seeking professional medical advice and the benefits of early diagnosis.
Transition: Seeking timely medical attention for potential colon cancer symptoms is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact prognosis and improve patient outcomes.
Tips for Recognizing Colon Cancer Symptoms
Early detection of colon cancer is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes. These tips can help you recognize the symptoms and take prompt action:
Tip 1: Pay attention to abdominal pain. Persistent or severe abdominal pain, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, warrants medical evaluation.
Tip 2: Watch for rectal bleeding. Blood in stool, whether bright red or dark, should be investigated promptly as it may indicate colon cancer.
Tip 3: Monitor bowel habits. Significant changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea lasting for several weeks, should not be ignored.
Tip 4: Be aware of unexplained weight loss. Unintentional weight loss of 10 pounds or more without an apparent cause may be a symptom of colon cancer.
Tip 5: Fatigue should not be dismissed. Persistent fatigue that interferes with daily activities may indicate underlying health issues, including colon cancer.
Tip 6: Nausea and vomiting can be signs. Persistent nausea and vomiting, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should be evaluated by a doctor.
Understanding these symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly can significantly improve the chances of early detection and successful treatment of colon cancer.
These tips emphasize the importance of recognizing colon cancer symptoms and taking proactive steps towards early diagnosis. In the next section, we will explore the benefits of screening and preventive measures for colon cancer.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of colon cancer is imperative for timely diagnosis and successful treatment. This article has explored the various symptoms associated with colon cancer, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and addressing them promptly. Abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting are common manifestations of colon cancer that should not be ignored.
Early detection remains crucial in improving patient outcomes. Regular screening, particularly for individuals at higher risk, can significantly increase the chances of detecting colon cancer at an early stage, when treatment is most effective. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and adopting a balanced diet, can also play a preventive role. Colon cancer screening and preventive measures empower individuals to take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing this potentially life-threatening disease.