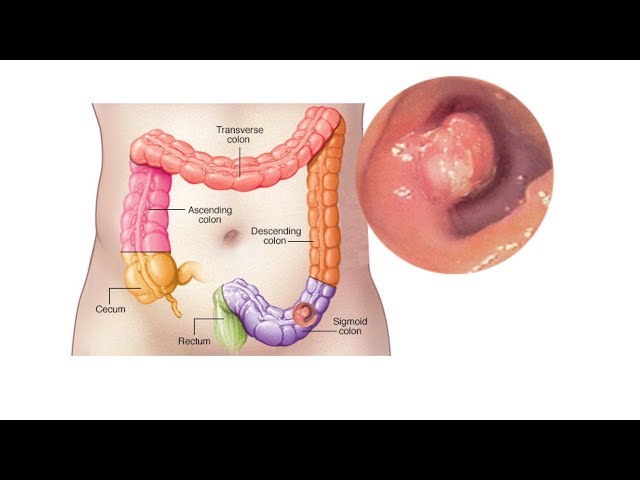
Colon cancer symptoms are physical signs and indicators that may suggest the presence of colon cancer, a type of cancer that develops in the large intestine. An example of a colon cancer symptom could be a persistent change in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation that lasts for more than a few weeks.
Recognizing colon cancer symptoms is crucial as it allows individuals to seek medical attention promptly, potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Early detection of colon cancer improves the chances of successful treatment and positive outcomes. A significant historical development in the field of colon cancer was the introduction of screening tests like colonoscopies, which have significantly reduced colon cancer mortality rates by enabling the detection and removal of precancerous polyps.
This article delves deeper into the various colon cancer symptoms, their significance, and the importance of seeking medical attention if any of these symptoms persist. Understanding the potential signs of colon cancer empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey and potentially reduce the risk of developing or progressing the disease.
Colon Cancer Symptoms
Recognizing and understanding the key aspects of colon cancer symptoms is essential for early detection and timely intervention, improving the chances of successful treatment and positive outcomes. These aspects encompass various dimensions related to the physical signs and indicators that may suggest the presence of colon cancer.
- Changes in bowel habits
- Blood in stool
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Narrow stools
These aspects are interconnected and can manifest differently in individuals. Changes in bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, are common symptoms. Blood in stool, whether bright red or dark, can indicate bleeding in the digestive tract. Abdominal pain, often accompanied by cramping or discomfort, may also be present. Weight loss, fatigue, and nausea can be associated with the body's response to cancer growth. Additionally, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, and narrow stools are other potential symptoms that warrant attention.
Changes in bowel habits
Changes in bowel habits are a common and crucial aspect of colon cancer symptoms, often signaling underlying issues within the digestive system. These alterations can manifest in various forms, each holding significance in the detection and diagnosis of colon cancer.
-
Frequency Changes
Individuals may experience a noticeable shift in the frequency of their bowel movements. This can range from more frequent bowel movements to less frequent ones, both of which deviate from the person's typical pattern.
-
Consistency Changes
Changes in stool consistency are another key indicator. Stools may become looser, harder, or narrower than usual, indicating potential disruptions in the digestive process.
-
Color Changes
The color of stools can also provide valuable insights. Blood in the stool, whether bright red or dark, is a common symptom of colon cancer and warrants immediate medical attention.
-
Urgency
A sudden and urgent need to defecate, often accompanied by a feeling of incomplete evacuation, can be a sign of colon cancer. This urgency may persist even after a bowel movement.
Collectively, these facets of changes in bowel habits serve as important indicators of potential colon cancer. Recognizing and promptly addressing these alterations can facilitate early detection and intervention, improving the chances of successful treatment and positive outcomes.
Blood in stool
Blood in stool, also known as hematochezia, is a significant aspect of colon cancer symptoms that warrants prompt medical attention. Its presence can manifest in various forms, each holding implications for understanding the underlying condition.
-
Color
The color of blood in stool can provide clues about its origin. Bright red blood typically indicates bleeding in the lower gastrointestinal tract, while dark red or maroon-colored blood may suggest bleeding higher up in the digestive system.
-
Amount
The amount of blood present in stool can vary, ranging from small streaks to large quantities. The volume of blood may correspond to the severity and location of the bleeding.
-
Consistency
The consistency of blood in stool can also offer insights. Fresh blood tends to be brighter in color and may appear as clots or streaks, whereas older blood may be darker and mixed with stool.
-
Accompanying symptoms
Blood in stool may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, or fatigue. These additional indicators can help provide a more comprehensive picture of the underlying condition.
Overall, the presence of blood in stool is a crucial symptom of colon cancer and should not be ignored. Understanding the different facets of blood in stool can aid in recognizing and promptly addressing this condition, leading to timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, a common symptom experienced by many individuals, can be a manifestation of various underlying health conditions, including colon cancer. Understanding the connection between abdominal pain and colon cancer symptoms is crucial for recognizing and promptly addressing this potentially serious condition.
Abdominal pain associated with colon cancer often presents as a dull, aching discomfort or cramping sensation in the abdomen. This pain may be intermittent or persistent, and its location can vary depending on the affected portion of the colon. The pain may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, or weight loss. Identifying the specific characteristics of abdominal pain can aid in differentiating it from other causes of abdominal discomfort.
In the context of colon cancer, abdominal pain serves as a critical component of the overall symptom profile. Its presence can indicate the growth of a tumor within the colon, which may obstruct the passage of stool or cause inflammation and irritation of the surrounding tissues. Recognizing abdominal pain as a potential symptom of colon cancer empowers individuals to seek medical attention promptly, leading to timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Understanding the connection between abdominal pain and colon cancer symptoms has practical applications in various healthcare settings. For instance, healthcare providers can utilize this knowledge to guide their diagnostic evaluations and determine the need for further investigations, such as colonoscopies or imaging studies. Additionally, educating individuals about the potential association between abdominal pain and colon cancer can promote early detection and reduce the risk of advanced disease progression.
Weight loss
Weight loss is a common symptom experienced by many individuals with colon cancer, often serving as a significant indicator of the disease's presence. This unintentional weight loss can result from various mechanisms associated with the growth and progression of colon cancer within the body.
One primary cause of weight loss in colon cancer is the disruption of normal digestive processes. As the tumor grows within the colon, it can obstruct the passage of food and waste, leading to reduced nutrient absorption and impaired digestion. This malabsorption can result in the body breaking down its own tissues, including muscle and fat, for energy, leading to weight loss.
Additionally, colon cancer can trigger systemic inflammation throughout the body, which can further contribute to weight loss. Inflammatory cytokines released by the tumor and immune cells can affect metabolism and appetite, resulting in decreased food intake and increased energy expenditure. This inflammation can also lead to muscle wasting and a breakdown of fat stores, exacerbating weight loss.
Recognizing weight loss as a potential symptom of colon cancer is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Individuals experiencing unexplained weight loss, particularly when accompanied by other symptoms such as changes in bowel habits or abdominal pain, should seek medical evaluation promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment of colon cancer can improve the chances of successful outcomes and reduce the risk of weight loss and other debilitating symptoms.
Fatigue
Fatigue stands as a prevalent symptom experienced by numerous individuals battling colon cancer, often manifesting as an overwhelming sense of tiredness and lack of energy. This unrelenting fatigue can significantly impact various aspects of daily life, including physical activities, cognitive functioning, and emotional well-being.
The connection between fatigue and colon cancer symptoms stems from several underlying mechanisms. Firstly, the presence of a tumor within the colon can disrupt the body's normal functioning, leading to an increased metabolic rate and energy expenditure. This heightened energy demand can deplete the body's energy stores, resulting in fatigue. Additionally, colon cancer can trigger systemic inflammation throughout the body, releasing inflammatory cytokines that further contribute to fatigue and malaise.
Real-life examples of fatigue within colon cancer symptoms abound. Individuals may experience persistent tiredness that interferes with their daily routines, making it challenging to engage in activities they once enjoyed. This fatigue can also manifest as difficulty concentrating, impaired memory, and reduced motivation. In some cases, fatigue can become so severe that it hinders individuals from carrying out essential tasks or maintaining social connections.
Understanding the connection between fatigue and colon cancer symptoms holds immense practical significance. Recognizing fatigue as a potential indicator of colon cancer empowers individuals to seek medical attention promptly, leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can not only improve treatment outcomes but also mitigate the debilitating effects of fatigue, enhancing the quality of life for those affected by colon cancer.
Nausea
Nausea, a common symptom experienced by many individuals with colon cancer, manifests as an unpleasant feeling of queasiness and an inclination to vomit. This distressing sensation can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort and interfering with various activities.
-
Stomach Discomfort
Nausea often presents as an uneasy feeling in the stomach, characterized by a churning or roiling sensation. This discomfort can range from mild to severe, potentially leading to gagging or vomiting episodes.
-
Loss of Appetite
Nausea can lead to a diminished desire to eat, as the thought or smell of food can trigger feelings of queasiness. This loss of appetite can contribute to weight loss and nutritional deficiencies if not adequately addressed.
-
Dehydration
Frequent nausea and vomiting can result in dehydration, as the body loses essential fluids and electrolytes. Dehydration can further exacerbate feelings of fatigue and weakness, impacting overall well-being.
-
Emotional Distress
The persistent presence of nausea can take an emotional toll on individuals, leading to anxiety, depression, and a diminished quality of life. This emotional distress can compound the physical discomfort associated with nausea.
These facets of nausea highlight its multifaceted nature and the impact it can have on individuals with colon cancer. Recognizing and managing nausea effectively is crucial for improving the overall well-being and quality of life of those affected by this condition.
Vomiting
Vomiting, a distressing symptom prevalent among individuals with colon cancer, involves the forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth. Its occurrence can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort and interfering with various activities. Understanding the multifaceted aspects of vomiting is crucial for recognizing and managing this symptom effectively.
-
Frequency and Severity
Vomiting can range from occasional episodes to frequent, debilitating occurrences. The severity may vary from mild regurgitation to forceful emesis, leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
-
Associated Symptoms
Vomiting in colon cancer patients is often accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. These symptoms can compound the discomfort and impact overall well-being.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies
Persistent vomiting can lead to nutritional deficiencies, as essential nutrients are lost. This can result in weight loss, electrolyte imbalances, and impaired immune function.
-
Emotional Distress
The persistent presence of vomiting can take an emotional toll on individuals, leading to anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life. This emotional distress can further exacerbate the physical discomfort associated with vomiting.
These facets of vomiting highlight its complex nature and the impact it can have on individuals with colon cancer. Recognizing and managing vomiting effectively is crucial for improving the overall well-being and quality of life of those affected by this condition.
Constipation
Constipation, a common digestive complaint, is characterized by infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stools. Its occurrence can be transient or chronic, with varying degrees of severity. In the context of colon cancer, constipation emerges as a significant symptom, often indicative of underlying abnormalities within the colon.
The connection between constipation and colon cancer symptoms stems from the mechanical obstruction caused by the tumor's growth within the colon. As the tumor enlarges, it can narrow the passageway, impeding the smooth passage of stool. This obstruction leads to constipation, characterized by infrequent and laborious bowel movements. Additionally, the presence of a tumor can disrupt normal colonic motility, further contributing to constipation.
Real-life examples of constipation within colon cancer symptoms abound. Individuals may experience infrequent bowel movements, with stools becoming hard, dry, and difficult to pass. Straining during bowel movements is common, often accompanied by a sense of incomplete evacuation. Chronic constipation can lead to the accumulation of stool within the colon, increasing the risk of complications such as fecal impaction and bowel obstruction.
Understanding the connection between constipation and colon cancer symptoms holds immense practical significance. Recognizing constipation as a potential indicator of colon cancer empowers individuals to seek medical attention promptly, leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications associated with advanced colon cancer. Moreover, managing constipation effectively can alleviate discomfort and improve the overall quality of life for those affected by colon cancer.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, characterized by loose, watery stools and increased bowel movements, emerges as a prevalent symptom in individuals with colon cancer. Its occurrence can range from mild and transient to severe and persistent, significantly impacting daily life and overall well-being.
The connection between diarrhea and colon cancer symptoms stems from the disruption of normal colonic function caused by the presence of a tumor. As the tumor grows within the colon, it can obstruct the passageway, leading to partial or complete blockage. This obstruction disrupts the normal absorption of water and electrolytes from stool, resulting in loose, watery stools and frequent bowel movements.
Real-life examples of diarrhea within colon cancer symptoms are common. Individuals may experience frequent episodes of loose, watery stools, often accompanied by abdominal cramps and urgency. The severity of diarrhea can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort, while others face debilitating symptoms that significantly impair daily activities.
Understanding the connection between diarrhea and colon cancer symptoms holds practical significance. Recognizing diarrhea as a potential indicator of colon cancer empowers individuals to seek medical attention promptly, leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications associated with advanced colon cancer. Moreover, managing diarrhea effectively can alleviate discomfort, improve quality of life, and support overall well-being for those affected by colon cancer.
Narrow stools
Narrow stools are a common symptom of colon cancer, resulting from various factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the colon. Understanding the multifaceted aspects of narrow stools is crucial for recognizing and managing this symptom effectively.
-
Size and Shape
Narrow stools are characterized by a significant reduction in diameter compared to the usual size. They may appear thin or ribbon-like, with a flattened or deformed shape.
-
Consistency and Texture
The consistency of narrow stools can vary. They may be hard and dry, resembling pebbles, or soft and mushy. The texture is often rough and uneven, with visible irregularities.
-
Frequency and Duration
Narrow stools can occur sporadically or persist for an extended period. The frequency and duration of narrow stools vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the colon cancer.
-
Accompanying Symptoms
Narrow stools can be accompanied by various other colon cancer symptoms, such as constipation, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits. These symptoms can provide valuable insights into the underlying condition.
Overall, narrow stools serve as an important indicator of colon cancer, often signaling the presence of a tumor or other abnormalities within the colon. Recognizing and promptly addressing narrow stools can lead to earlier diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and improved outcomes for individuals affected by colon cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions about Colon Cancer Symptoms
This section aims to address common queries and clarify various aspects of colon cancer symptoms, providing valuable information to enhance understanding and empowering individuals to take proactive measures for early detection and management.
Question 1: What are the most common colon cancer symptoms?
The most common colon cancer symptoms include persistent changes in bowel habits, such as constipation, diarrhea, or narrow stools; blood in stool; abdominal pain and cramping; unexplained weight loss; fatigue; and nausea and vomiting.
Question 2: Can colon cancer symptoms appear gradually or suddenly?
Colon cancer symptoms typically develop gradually over time as the tumor grows and affects the colon's normal functioning. However, in some cases, symptoms may appear more suddenly, especially if the cancer has progressed to an advanced stage.
Question 3: How often should I get screened for colon cancer?
Regular colon cancer screening is recommended for individuals at average risk starting at age 45. The frequency of screening may vary based on individual risk factors and family history. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate screening schedule for you.
Question 4: What should I do if I experience any colon cancer symptoms?
If you experience persistent colon cancer symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention significantly improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Question 5: Can colon cancer symptoms be managed?
Yes, many colon cancer symptoms can be managed effectively with appropriate medical interventions. Treatment options vary depending on the stage of cancer and the specific symptoms experienced. Management strategies may include dietary modifications, medications, and surgical procedures.
Question 6: Are there any lifestyle factors that can reduce the risk of colon cancer?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to reducing the risk of colon cancer. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use are all important preventive measures.
These FAQs provide essential insights into colon cancer symptoms, emphasizing the importance of early detection and appropriate management. If you have any concerns or experience persistent symptoms, do not hesitate to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
The following section will delve deeper into the diagnosis and treatment options available for colon cancer, offering valuable information to empower individuals in their healthcare journey.
Tips for Managing Colon Cancer Symptoms
Understanding and managing colon cancer symptoms is crucial for improving quality of life and overall well-being during treatment. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate these symptoms effectively:
Tip 1: Stay hydrated
Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to prevent dehydration caused by diarrhea or vomiting.
Tip 2: Manage pain
Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can provide relief from abdominal pain.
Tip 3: Adjust your diet
If experiencing diarrhea, opt for BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, toast) and avoid spicy or fatty foods.
Tip 4: Control nausea and vomiting
Anti-nausea medications or ginger tea can help reduce feelings of nausea and vomiting.
Tip 5: Rest adequately
Fatigue is a common symptom; ensure you get enough rest and avoid overexertion.
Tip 6: Seek support
Connect with support groups or counselors to share experiences and gain emotional support.
Tip 7: Follow medical advice
Adhere to your doctor's recommendations for medications, lifestyle changes, and follow-up appointments.
Summary: By implementing these tips, you can effectively manage colon cancer symptoms, improve your quality of life, and support your overall well-being during treatment.
The following section will provide insights into the latest advancements and research in colon cancer treatment options, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
Conclusion
This comprehensive exploration of colon cancer symptoms has illuminated various key points. Firstly, recognizing the common symptoms, such as changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, and abdominal pain, is essential for early detection and prompt medical attention.
Secondly, understanding the mechanisms behind these symptoms, including tumor growth and obstruction, empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. Thirdly, proactive management of symptoms through lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and medications can significantly improve quality of life during treatment.
As research continues to advance our understanding of colon cancer, it is crucial to prioritize regular screening, especially for individuals at higher risk. Early detection remains the cornerstone of successful treatment outcomes. By raising awareness, encouraging preventative measures, and supporting those affected by colon cancer, we can collectively work towards a future where this disease is effectively managed and its impact is minimized.