Cervical cancer occurs most often in women aged 40 years or older. Cancer cells are unspecialized and do not develop into cells of a specific type.
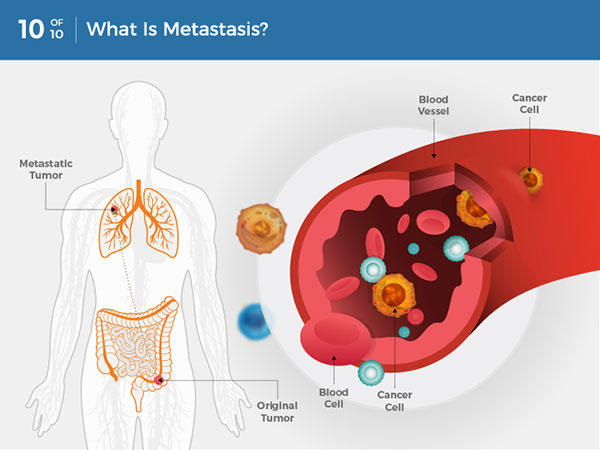 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
how often do cancer cells occur is important information accompanied by photo and HD pictures sourced from all websites in the world. Download this image for free in High-Definition resolution the choice "download button" below. If you do not find the exact resolution you are looking for, then go for a native or higher resolution.
Don't forget to bookmark how often do cancer cells occur using Ctrl + D (PC) or Command + D (macos). If you are using mobile phone, you could also use menu drawer from browser. Whether it's Windows, Mac, iOs or Android, you will be able to download the images using download button.
Similar to stem cells cancer cells proliferate or replicate many times for long periods of time.

How often do cancer cells occur. It multiplies and multiplies until instead of 2 abnormal cells you now have 2 billion abnormal cells in the form of a tumor or cancer. If any of these signals are faulty or missing cells may start to grow and multiply too much and form a lump called a tumour. In order for oncogenic mutations to induce cancer they must occur in dividing cells so that the mutations are passed on to many progeny cells.
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Cancer is not common in young adults but a wide variety of cancer types can occur in this age range and treating these cancers can be challenging for a number of reasons. Normal cells divide in an orderly way.
Instead cancer cells rely on glucose sugar by about 5 to 10 times more than normal cells for their primary energy producing pathway. When such mutations occur in nondividing cells eg neurons and muscle cells they generally do not induce cancer which is why tumors of muscle and nerve cells are rare in adults. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump abnormal bleeding prolonged cough unexplained weight loss and a change in bowel movements.
How does cancer occur. Cancer cell proliferation is rapid and excessive as these cells spread throughout the body. It either grows too fast multiplies too often or spreads to a place it.
This is because cells produce signals to control how much and how often the cells divide. They crowd out normal cells. A primary tumour is where the cancer starts.
Most cancers occur in older adults. Precancerous cervical changes affect cells on the surface of a womans cervix. Some types of cancer called leukaemia start from blood cells.
From that event on the cell is never the same and doesnt do its job right. Cancer is when the cells start to grow out of control. These contrast with benign tumors which do not spread.
They die when they are worn out or damaged and new cells take their place. Glucose is converted into lactic acid which is then recycled back into glucose by the liver. Cancer causes cells to divide uncontrollably.
But for statistics purposes cancers in young adults are often thought of as those that start between the ages of 20 and 39. The cancer cells keep on growing and making new cells. Cancer cells do not require the consumption of oxygen in order to produce energy as do normal cells.
Now i separate. If abnormal cells spread deeper into the cervix or to other tissues or organs the disease then becomes cervical cancer invasive cervical cancer or metastatic cancer. The cells in our bodies all have certain jobs to do.
This can result in tumors damage to the immune system and other impairment that can be fatal. In the united states an estimated 155 million people with a history of cancer were living as of january 1 2016 according to a 2018 report from the american cancer society.
 Cell Division Cancer Learn Science At Scitable
Cell Division Cancer Learn Science At Scitable
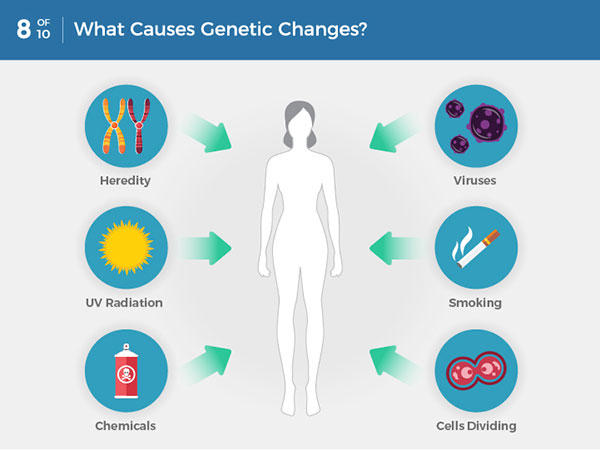 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
645x822.png) What Causes Cancer Cancer Institute Nsw
What Causes Cancer Cancer Institute Nsw
 The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To
The Cell Cycle In Cancer Developing Cancer Therapies To
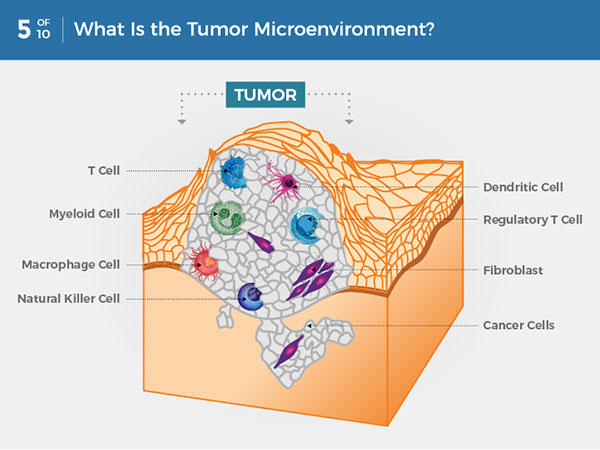 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
 Cancer Overview Causes Treatments And Types
Cancer Overview Causes Treatments And Types
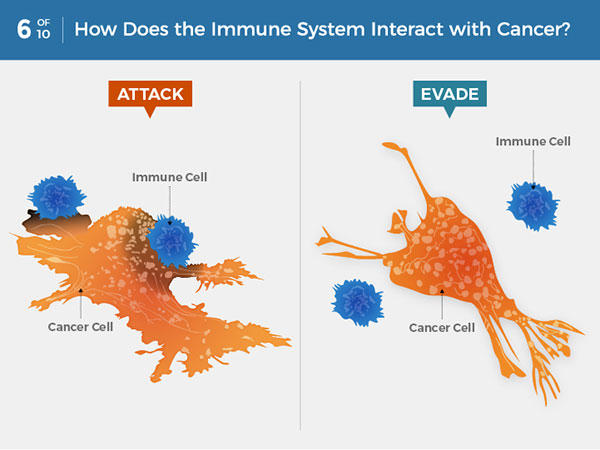 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
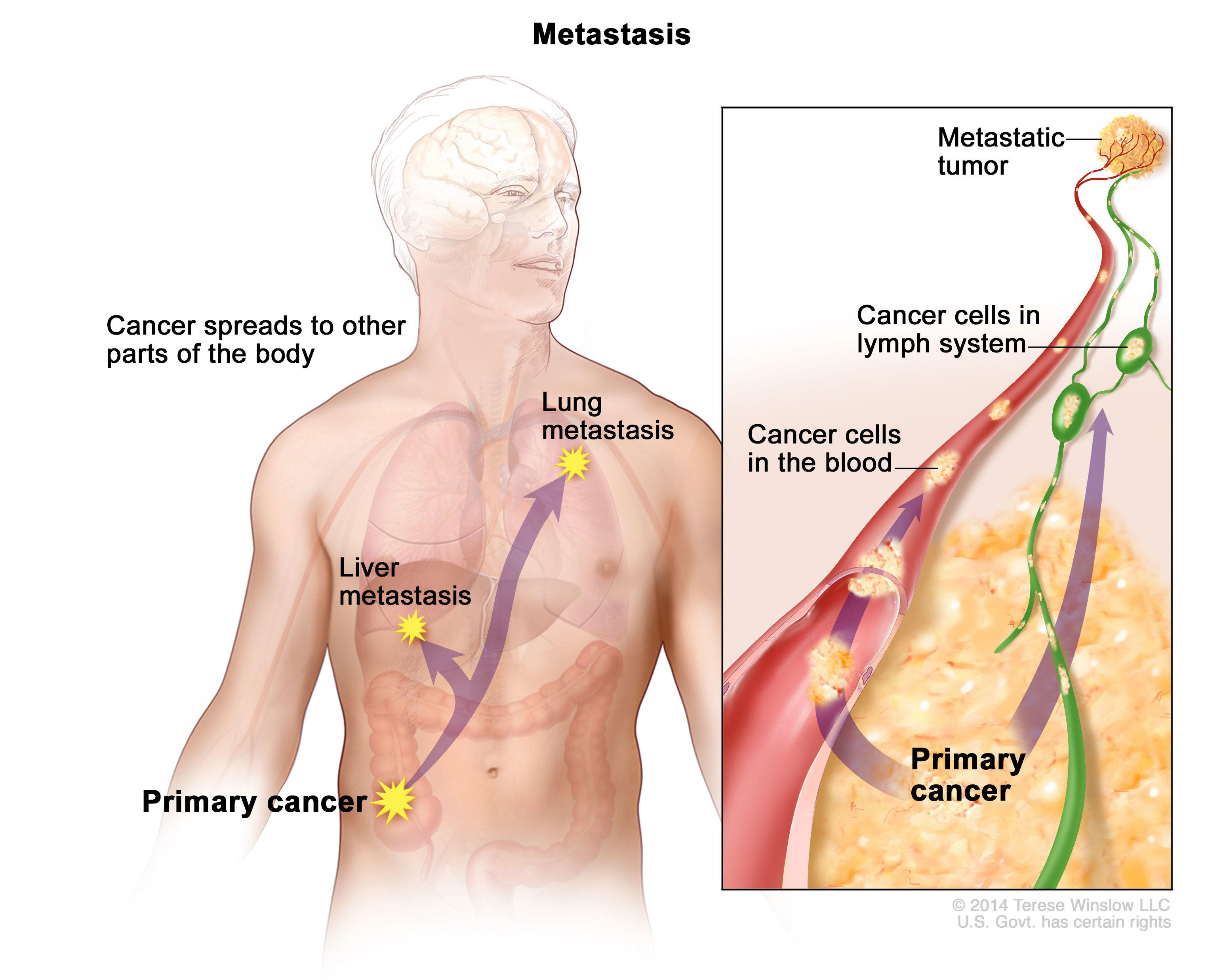 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
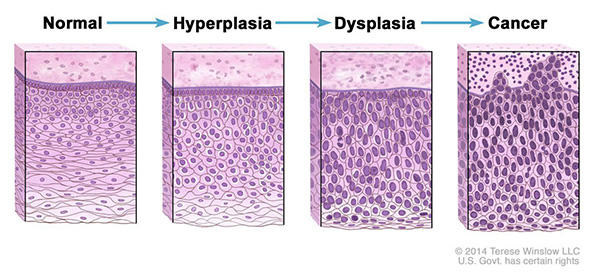 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
 What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
What Is Cancer National Cancer Institute
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/illo_normal-cells-cancer-cells-596cdd256f53ba00111a65bb.png) Cancer Cells Vs Normal Cells How Are They Different
Cancer Cells Vs Normal Cells How Are They Different
